
Extrinsic factors

Even Everton Can Score Tonight
Environment
Equipment

Performance Equipment
Some equipment in sport is used to enhance performance. Rock climbers use a harness to support their body weight. Golfers use the latest clubs with the latest technology to improve performance.

Clothing/Footwear
Wearing the correct clothing and footwear will also reduce the chance of an injury. Football boots help to prevent you from slipping when playing on wet surfaces. Running spikes help with grip when sprinting and climacool clothing helps to keep you cool during hot days and helps to prevent over heating.
Coaching/Supervision

Coaching/Supervision
Poor coaching and supervision of activities can lead to performers being taught the incorrect technique e.g. a gymnastics coach teaching someone how to do a somersault could lead to a muscle sprain if they perform the technique incorrectly. If the coach has ineffective communication e.g. a coach is unable to simplify their language when coaching a group of children resulting in them misunderstanding instructions and then mishandling sporting equipment and injuring themselves. Coaches must also ensure that all participants are aware of the importance of adhering to rules and regulations to avoid injury from occurring.

Examples
1. A gymnastics coach incorrectly explaining how to perform a somersault could cause injury such as a sprain or strain.
2. A rugby coach incorrectly explaining how to tackle can lead to contusions, abrasions or concussion.
Safety Hazards

Risk Assessments
Method of looking at playing area, equipment, activities etc. and deciding on control measures to prevent injury from occurring.
If the playing area was not safe then you should not allow people to play or else you are at risk of causing an injury. Examples of when the playing area is not safe could be if the playing surface is too slippery due to rain, too hard due to cold weather or may just be covered in litter.

Safety Checks
Safety checks: For example, the referee checking the field for glass in football, a climbing instructor checking a harness is not damaged before it is worn.

Emergency Action Plan
Plan of how to respond if an emergency was to occur. Including information on: name of first aider on site, mobile available for calling emergency services? Is a first aid kit available? Can the ambulance access the site of the injury?
Type of activity

Non contact sports
Non contact sports such as running are more likely to cause chronic injuries such as shin splints.
Wearing correct footwear, warming up properly and allowing sufficient rest time will prevent such chronic injuries.
intrinsic factors
P.I.P.P.S
PHYSICAL PREPARATION
PHYSICAL PREPARATION

Over Training
Overtraining can put too much stress on the body when it may not be physically ready e.g. a marathon runner returning from injury and running a marathon in the first week back. Incorrect training e.g not allowing muscles to recover from exercise can also lead to muscle pain and stiffness resulting in chronic injuries.

Warm Up
Failing to warm up or warming up incorrectly can lead to muscle strains due to not allowing blood to flow to the muscles or increasing the flexibility of muscle fibres. The body is therefore not prepared to take part in exercise.

Cool Down
Helps to keep the blood circulating to stop blood from pooling and helps to remove waste products from the muscles. This helps to reduce the likelihood of muscle pain and swelling from occurring.

Fitness Levels
When individuals are involved in sport regularly they are more likely to suffer from sports injuries. This is particularly common in weight bearing exercises such as running due to the impact on the feet, ankles and shins. Lower fitness levels are linked more to an increase in medical conditions such as heart disease and diabetes rather than sports injuries.

Overuse
Overuse refers to using the same muscles over and over again. An overuse injury is any type of muscle or joint injury, such as tendonitis or a stress fracture, that's caused by repetitive trauma. An overuse injury typically stems from: Training errors. Training errors can occur when you enthusiastically take on too much physical activity too quickly.

Muscle Inbalance
Muscle imbalances occur when occur when one muscle is stronger than its opposing muscle e.g. the hamstrings and the quadriceps. When your muscles become imbalanced, the stronger muscles overcompensate for the weaker ones. Because the weak muscles can’t match the strength and endurance of the stronger ones, they fatigue more easily and force the stronger muscles to work harder. Over time, the muscles begin to break down under the strain and develop overuse injuries.
INDIVIDUAL VARIABLES
How does individual variables link to injury???
Age, Gender, Flexibility, Nutrition, Sleep, Re-occuring Injuries


PSYCHOLOGICAL FACTORS
Motivation:
Motivation is a combination of the drive within us to achieve our aims and the outside factors which affect it. Motivation has the following two forms, intrinsic motivation and extrinsic motivation.
Intrinsic motivation – Motivated by the feeling of pride and enjoyment when you have been successful. Inner desire to overcome a problem or task.
Extrinsic motivation – Motivated by external sources outside of the performer e.g. money, rewards, trophies, praise from others, recognition etc.
If you are under motivated and are not motivated by trophies, praise or rewards you may lack concentration and focus during a sporting activity, for example in boxing this could cause a boxer to drop his guard and be hit by the opponent resulting in a facial injury such as a cut or bruise. If you are over motivated and are desperate to be rewarded with an intrinsic or extrinsic reward, this could also result in an injury occurring, for example, a losing team in the cup final in football could end up fouling a player in the penalty box due to them desperately trying to prevent the opposition from scoring a goal. This would not only result in a penalty to the other team but could cause an injury to the opponent or themselves for sliding in and possibly using the incorrect technique due to being over motivated.
Aggression:
Aggression is defined as “any form of behaviour directed toward the goal of harming of injuring another live being who is motivated to avoid such treatment” This can be divided into two parts; hostile and instrumental. Hostile aggression is where the main aim is to cause injury or harm to an opponent. Instrumental aggression is to achieve a goal by using aggression e.g. a rugby player using aggression to tackle an opponent to win the ball. An example of aggression causing an injury could be in a rugby match a player may retaliate to a hard tackle by punching an opponent. This could be as a result of not agreeing with the tackle or because they are losing. This type of aggressive act could lead to a bruise, cut or fracture.

Arousal:
Arousal is an individual’s level of excitement and readiness to perform. Over arousal is where a performer can feel overly ‘psyched up’ for a game or match. This could cause an individual to perform hard and untimed tackles in e.g. football due to being over excited and over aroused. Under arousal is on the opposite end of the continuum and would be associated with characteristics whereby a performer appears to be acting lazy, sluggish and not prepared for the activity. In a sport such as rugby this could lead to injury as a person may not react quickly to oncoming players who may tackle them. Being unprepared in this way could lead to the player falling awkwardly and injuring themselves.
Anxiety:
Anxiety is a feeling of worry, nervousness or unease about something with an uncertain outcome. An athlete suffering from anxiety will usually underachieve. In sport anxiety is linked to a lack of concentration and focus. This could cause a sports injury in basketball as the player may not be focusing on the game. A team mate could try to pass the ball to them but due to a lack of focus this could cause them to become injured by the ball due to not focusing and catching the ball. This could cause an acute injury such as bruise.
POSTURE
Posture is the position in which you hold your body upright against gravity while standing, sitting or lying down. Good posture involves training your body to stand, walk, sit and lie in positions where the least strain is placed on supporting muscles and ligaments during movement or weight-bearing activities.
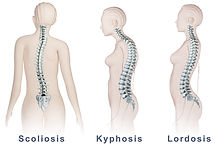
Causes of poor posture:
-
Poor stance / gait (walking pattern): For example, bending your knees or hunching your shoulders when standing
-
Sitting positions: For example, slumping / slouching on the sofa rather than sitting upright
-
Physical defects: For example, muscles which are weakened around an injured area from a previous injury
-
Lack of exercise: Lack of core muscle strength means less support. Another example would be when someone is overweight which puts strain on posture.
-
Fatigue (tiredness): Tired muscles are unable to support the skeleton properly and cause people to slouch.
-
Emotional factors: For example, when people have low self esteem / lack of confidence, this can affect posture. People suffering from these factors tend to slouch, look down when walking and have hunched shoulders.
-
Clothing / footwear: For example, wearing shoes with high heels causes people to lean forward which affects their posture.
Sports injuries related to poor posture
■Pelvic tilt – This is the orientation of the pelvis which can be towards the front, back or either side of the body.
■Lordosis – LO for lower - An inward curvature of the spine at your lower back.
■Kyphosis – K for KING - Curvature of the spine at the top.
■Round shoulder – Think QUASIMODO - Caused by slouching.
■Scoliosis – S SHAPE - Twisting and curvature of the spine towards the side.





